The Industrial Metaverse: Digital Twin, the Killer Application Set to Change All Industries

In the realm of metaverse technologies, one application stands out as a true game-changer, even though it lacks glamorous media coverage and the allure of science fiction.
The industrial metaverse has quietly emerged as a transformative force, already making tangible differences across various business sectors today.
While the discourse on the metaverse has centered on themes such as immersive gaming, social interactions, retail experiences, and remote work, it’s the cornerstone sectors of the economy—transportation, manufacturing, and construction, to name a few—that are spearheading practical and impactful use cases.
These industries are proactively integrating metaverse-like solutions to enhance decision-making in multiple facets of their operations. But that’s not all.
The potential of the industrial metaverse extends far beyond these sectors alone. In fact, it holds the promise of revolutionizing every industry, paving the way for an all-encompassing and seamlessly interconnected digital world.
What is the industrial metaverse? And how does it differ from the “conventional” metaverse?

So what is the difference between the industrial metaverse and the traditional concept of the metaverse?
The metaverse, at its core, represents a virtual reality-driven, three-dimensional iteration of the internet. It’s a computer-generated world consisting of ever-present and interoperable digital environments that enable individuals to engage in everyday activities, such as socializing, working, and learning, with greater ease and efficiency than the current internet and brick-and-mortar infrastructures allow.
However, existing metaverse-like environments are fragmented, each offering limited functionality catering to specific domains. While there are metaverses dedicated to immersive gaming, social media, fitness, retail, and education, none come close to achieving the all-encompassing vision depicted in science fiction.
The industrial metaverse, on the other hand, mirrors the persistent nature of the real world. Its fundamental objective is to enhance efficiency and safety within industrial sectors by creating real-time virtual replicas of machines, factories, utility grids, traffic networks, and other complex systems.
Through this replication, industries gain the ability to test and optimize operation processes before implementing them in the physical realm, driving improvements across the board.
Imagine a global sports apparel manufacturer with suppliers, factories, logistical hubs, and sales distribution networks spread across the globe. What if this company needs to shut down a specific facility due to geopolitical instability or introduce new equipment to scale production? With the industrial metaverse, the company can simulate these adjustments and investments, replicating its employees, assets, and workflows in virtual reality.
This digital replica is programmed to follow real-world parameters, consisting of corporate accounting, economics, physics, communications, and any law and regulation to anticipate the benefits and drawbacks.
The Internet of Things (IoT), sensors, and workers positioned throughout the real-world supply chain continuously collect and relay data to its metaverse counterpart. Worldwide stakeholders seamlessly collaborate even when they’re apart. Simulations even let decision-makers “go back in time” to examine past failures and “travel into the future” to project outcomes.
Powering the industrial metaverse is the concept of the digital twin, which serves as its technological backbone.
So, what exactly is a digital twin, and how does it work?
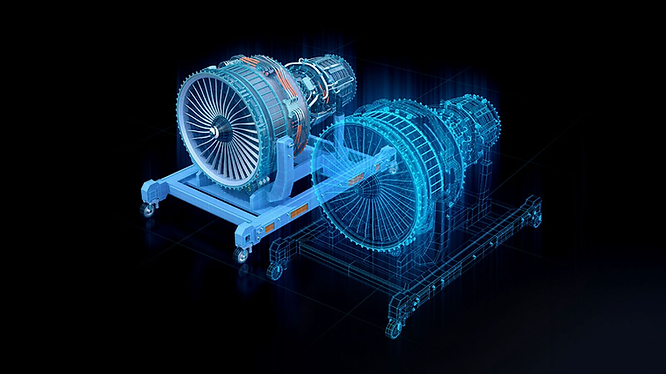
A digital twin is a virtual reality replica of an object, process, or environment that closely mimics its counterpart in the physical world. It’s always on and mirrors everything in real-time.
The technology can be applied to anything from a race car engine or global logistics to even an entire nation. An industrial metaverse typically consists of multiple interconnected digital twins.
Initially deployed as simulation models for product management to track and predict lifecycles, digital twins were helpful for anticipating risks and opportunities before committing resources.
With the advent of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), immersive devices, IoT solutions, enhanced computing power, and lightning-fast networks, digital twins are now being adopted on a much larger scale.
For instance, automobile maker BMW has leveraged digital twins to create virtual replicas of its manufacturing sites, streamlining various aspects of its business operations. The benefits are already evident in areas such as human resource training, assembly line optimization, resource allocation, and integration of new products. The company has even taken the bold step of “pre-constructing” an entire factory within its industrial metaverse, allowing for simulations to be conducted before physical construction commences.
Here are other notable examples highlighting the significant impact of the industrial metaverse:
The industrial metaverse and manufacturing.
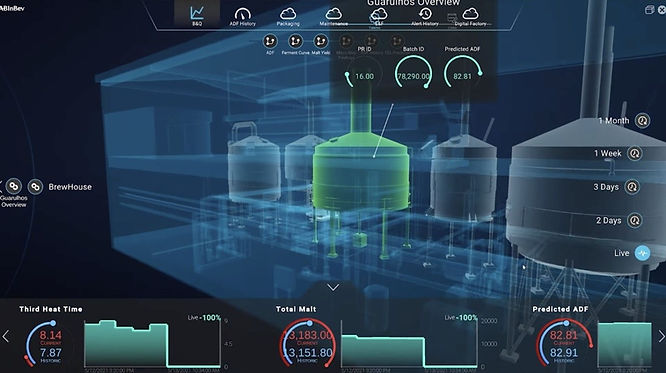
Brewing giant Anheuser-Busch InBev has harnessed digital twin technologies to construct an industrial metaverse tailored to its brewing and supply chain operations.
Through the virtual replicas, the company can make informed decisions based on real-time, company-wide, and external conditions, enabling efficient ingredient utilization and resolving production line bottlenecks efficiently.
Additionally, front-line engineers are equipped with mixed reality devices that facilitate live troubleshooting, enhancing overall productivity.
The industrial metaverse and urban planning.
Virtual Singapore is a collection of digital twins of the city-state. Constructed based on real-time, dynamic, and topographical data, it has been operational for nearly a decade, reshaping the landscape of smart urban planning.
Government agencies, private companies, academic organizations, and citizens have leveraged this powerful tool for planning a wide range of initiatives, from smart energy grids to real estate development, or even a fun day of shopping.
VR headsets and the industrial metaverse.

VR headsets reign supreme as the ultimate tool to capitalize on all the advantages the industrial metaverse offers. These head-mounted devices provide immersive experiences, allowing users to visualize complex industrial processes, engineering designs, and data in three dimensions.
Furthermore, users can intuitively manipulate objects, operate machinery, and precisely simulate real-world scenarios by interacting and navigating in virtual reality via hand controllers, gesture recognition, eye tracking, or even full-body tracking.
With continual advancements in graphics fidelity, tracking precision, wearer comfort, and affordability, VR headsets will play a critical role in the industrial metaverse’s adoption and use case expansion.
Headset maker HTC VIVE is leading the way in offering a comprehensive portfolio of VR headsets, including PC VR options for top-tier immersive experiences and the recently launched standalone VIVE XR Elite. Learn more about some of the very best VR headsets currently available.
Industry 4.0: the future of industrial metaverse.
The industrial metaverse finds itself at the forefront of the fourth industrial revolution, or Industry 4.0.
From the steam-powered machines of the original industrial revolution in the late 1700s to early 1800s, to the advent of electricity and mass production assembly lines in the second, and the subsequent computerization and automation of the third, each era has brought forth transformative advancements. Industry 4.0 builds upon these developments, harnessing the power of intelligent systems and data analytics made possible by AI and ML technologies.
According to Emergen Research, the global digital twin market is projected to reach an astonishing value of US $106.26 billion by 2028, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 54.7%.
The industrial metaverse has become a vital component if Industry 4.0 is to maintain its transformative trajectory. More and more manufacturers are creating intricate systems of interoperable digital twins, essentially forming private industrial metaverses.
The future of the industrial metaverse lies in the intersection of rapidly advancing technologies and disciplines, some of which are still in the wild-wild-west stages of development. Augmented and virtual realities, 3D imaging, edge and cloud computing, big data analytics, data centers, renewable energy, industrial IoT, AI, ML, and 5G networks are just a few examples.
Imagine the computing power and data storage capacity required to process a photorealistic, three-dimensional, and immersive environment that replicates the complexity of a metropolitan subway system or an offshore wind farm.
Moreover, the staggering amount of data collected by tens of thousands of sensors, IoT devices, and workers needs to flow back and forth between physical and digital realms in real-time, enabling meaningful analysis and informed decision-making. All of this must be achieved without exacerbating the global climate crisis, raising further questions about sustainable power sources for data centers, processing chips, and immersive hardware.
While the industrial metaverse is already transforming numerous industrial sectors, its potential remains immeasurable. One potential scenario involves widespread adoption of smaller-scale digital twins until every company asset and process is copied and interconnected—an entire organizational ecosystem within an industrial metaverse.
Ultimately, the vision of the industrial metaverse encompasses multiple interconnected company metaverses forming industry-specific metaverses, which, in turn, converge to create an economy-wide metaverse and so forth.